What You Know about the Cyber Security of NFT

Previously, we have introduced the non-fungible token (NFT) and how to protect crypto wallets. This time, we will discuss the ecosystem of NFT as well as various related parts that can be attacked or defrauded by criminals, and the corresponding security advice.
Why does NFT become popular?
A NFT can be regarded as analogous to certificate of ownership, which represents the asset you own. At present, most of the hot-selling NFTs are mainly based on avatar pictures. The sellers attract buyers with unique designs and limited sales skills. Buyers can put it on social media to show they are one of the owners of the pictures and enhance their sociability. Also the current development of asset types is extending to cover physical ones, like artworks or real estate projects, which have made NFT an eye-catching keyword. Hence, owning NFT has become a symbol of social status, drawing more people to participate in.
Ecosystem of NFT
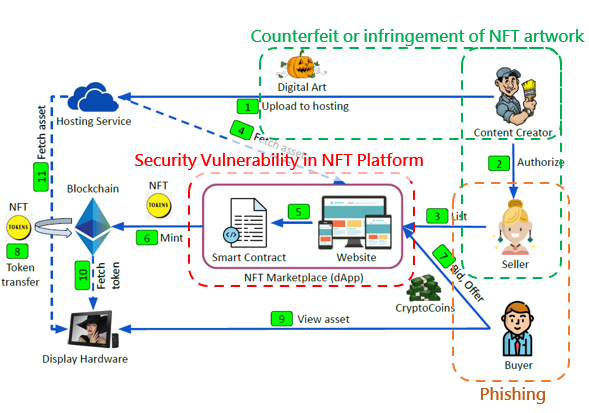
NFT is an ownership record stored on the blockchain, which only accounts for the last part of the entire ecosystem. The entire ecosystem is first initiated by creators, who create digital works. Then, sellers and buyers will auction and trade their favourites on the NFT platform. After the buyer signs the transaction, the platform will write the transaction record into the blockchain, including the transfer of amount and the ownership of the artwork [1].

Source: Understanding Security Issues in the NFT Ecosystem, November 2021, University of California, Santa Barbara [1]
With the NFT boom and the rise in value, many people will upload their personal works to the NFT platform for investment and auction. In view of this, criminals will use various methods to attack the weaknesses in the ecosystem to steal other people’s NFT assets or even cryptocurrencies.
Recent NFT Cyber Security Incidents
At the end of December 2021, the famous Monkey King-themed NFT project “Monkey Kingdom” was hacked in the instant messaging platform Discord. A hacker posing as a group administrator posted a fake link, which was a phishing website. Users clicked on the link without paying careful attention to the URL, and the SOL (a cryptocurrency) in the crypto wallet was stolen, and the total amount involved about 1.3 million US dollars[2] (around 10 million HK dollars).
Announcement on the discord hack pic.twitter.com/1r7svjlZcB
— Monkey Kingdom (@MonkeyKingdom_) December 21, 2021
Source: https://twitter.com/monkeykingdom_/status/1473326864899141632
Also, in February 2022, a hacker sent out emails impersonating OpenSea, one of the biggest NFT trading platform, to conduct a phishing attack, tricking users into signing problematic smart contracts and sending crypto assets to the hacker’s wallet. A total of about $1.7 million was stolen from the affected users[3] as a result (around 13 millions HK dollars).
Our team has been working around the clock to investigate the specific details of this phishing attack. While we haven’t yet determined the exact source, we wanted to share a couple of EOD updates:
— OpenSea (@opensea) February 21, 2022
🧵
Source: https://twitter.com/opensea/status/1495625768713469954
Moreover, in mid-January of the same year, a user discovered a security vulnerability on the OpenSea website. Users can buy NFT assets with less than 1% of price floor, such as those from the Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC), causing serious loss to the original creators[4].
Apart from website vulnerabilities causing losses to the original creators, NFT torts are also rampant. The famous sports brand, Nike, filed a lawsuit to StockX, a second-hand trading platform, alleging it to have minted the brand trademark to be NFTs without consent, and hoped to make profits by Nike's popularity[5].
Types of attacks on NFT and related platforms
Hence, most of the attacks are targeting the users and the NFT platform. They can be classified into the following three categories:
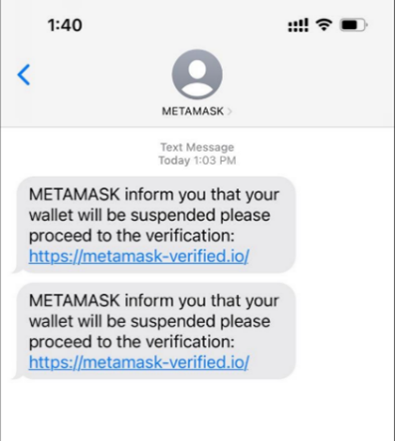
Phishing
Stealing recovery phrase of crypto wallet
A hacker sends a fake website link via email, text message or Discord. The fake website has the same layout as the real crypto wallet site and asks the wallet user for the recovery phrase. The hacker obtains the phrase and has full control over the cryptocurrency in the encrypted wallet. In addition to fake websites, other methods include impersonating technical support personnel to offer assistance but actually aiming to trick for the phrases.


A fake transaction message transfers wallet asset
The fake platform will pop up a transaction message to request the victim to connect the wallet, sign and confirm the transaction. But the transaction is actually to transfer assets to the hacker’s account.
Security Vulnerability in NFT Platform
A NFT platform, which is developed and operated by the vendor, operates similar to that of an online shopping platform,. There are many popular NFT platforms on the Internet, and vulnerabilities are usually caused by insufficient security consideration during the design and development phrases. Such vulnerabilities become the hackers’ targets. For example, a hacker can upload artworks containing malicious code[6], hack into accounts without two-factor authentication[7], or trade NFTs at low prices and resell them for profit through security design flaws.
Counterfeit or infringement of NFT artwork
Most of the NFT artworks are pictures, and the hot sale of NFTs also attracts plagiarists to “steal pictures” and sell them on other platforms[8].
At present, there are no regulations around the world to govern the trading of NFTs, and there is a general belief that NFTs only represent the ownership of assets but not the copyright. The unclear rights of NFT owners and the difficulty in pursuing them cause mental distress and monetary losses to those who have purchased counterfeit or infringing NFTs.
How to trade NFTs securely
HKCERT recommends that users should adopt the following security measures:
Do not click any links or attachments in emails, text messages or social media from unknown sender
Use the browser bookmark function to store the NFT platform URL
Avoid using links sent by others to log in to the platform
Enable two-factor or multi-factor authentication
Never disclose your wallet’s recovery phrase to a third party
Set up a temporary wallet and only store a suitable amount of cryptocurrency for trading
Carefully verify all information before signing any smart contract, understand the terms and potential risks
Review the permission which is granted to access your NFT and revoke past authorisation for uncertain purpose
Conduct sufficient research before purchasing NFT. Verify the identity of the designer, and check whether information of the NFT is complete (for instance, users’ reviews, past transactions, whether it is an original work, etc.)
If the platform has a mechanism for removing infringing NFTs, users can check with the corresponding system administrator
Other considerations
Use the Discord carefully
Many NFT sellers use Discord for publicity. It is convenient for users to gather and publish news. Since the platform supports real-time chat among many users with nickname. It is easy to be leveraged by hackers to confuse users. In one of the incidents, a hacker impersonated a seller to distribute phishing links and caused financial losses[9].
For general users
- Carefully verify information that differs from official public one
- Check website links carefully, such as comparison with suspicious and official URLs
- If you find the NFT value on the platform is different from the official announcement, you should be vigilant
- Disable the Direct Message function to avoid spammer
For platform administrators
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Set permissions for individual managers
- Review admin tool permissions
Be aware of the risks of storage of the NFT artwork
NFT artworks are usually uploaded to network storage by creators, and users access through links. Generally, the storage methods are:
Store on the same blockchain
Because the data of the blockchain is immutable, user can maintain persistence access. However, this method can significantly increase transaction fees.
Store on another blockchain or decentralised storage (e.g., IPFS, Arweave)
A decentralised storage also has the characteristics of immutability, but the artwork is still subject to the risk of being removed. In addition, some platforms will charge a fee.
On private or centralised servers (e.g., cloud)
If the site no longer hosts the artwork or the link is changed, the link will be broken and the NFT will become worthless.
Therefore, users should also pay attention to the storage method of NFT Metadata and artworks before participating in NFT trading. Users can find the storage location of NFT artworks by using a free blockchain explorer platform such as etherscan or polyscan, or checking with the sellers directly.
Reference
[7] https://www.vice.com/en/article/v7mw7b/nifty-gateway-hacked-nfts
[8] https://postergrind.com/can-nfts-be-copied-7-things-to-know
Related Tags
Share with

