IoT Security Guideline for Digital Signage

1. Introduction
With the rapid development of digital display panel technology, digital signage has become an important Internet of Things (IoT) device for modern businesses to disseminate public information and brand promotions. There are many types of digital signage for wide range of applications, e.g. information displays, electronic billboards, interactive systems, digital advertisement panels, etc.
These highly interconnected display systems, through the Internet of Things (IoT) technology, have achieved remote content management, real-time information updates and interactive functions, greatly enhancing the flexibility and effectiveness of advertising and information dissemination. However, due to their network connectivity, digital signage is also vulnerable to a series of cybersecurity challenges, which might affect the normal operation of signage, and endanger the network and data security connected to them.
To address these challenges, this guideline aims to provide best practices and security measures for digital signage users, operators, advertisers and technology providers, in order to enhance the safety and privacy of the public, also ensure the long-term sustainable development of digital signage technology.

Various types of digital signages (image source: iStockPhoto)
2. Potential Threats
Data Leakage
Sensitive information stored in the digital signage may be accessed by unauthorised third parties, and data in transit (e.g. when updating content) may be intercepted.
Malware Infection
The system of the digital signage may be implanted with viruses, trojans or other malicious programs, which may result in system malfunctions, inappropriate displays, etc. Malware may also be introduced through the USB port or network connection, which may affect the normal operation of the digital signage.
Unauthorised Access
Hackers may remotely control the digital signage system to change the display content or functions. Weak passwords or insecure authentication mechanisms may be easily exploited, resulting in unauthorised operation of the digital signage.
Content Defacement
Information displayed on the digital signage may be tampered with, resulting in the dissemination of incorrect or misleading information on displays in public places and the system may be hijacked for other advertising or promotional purposes.
System Tampering
The hardware, software and configuration settings of the digital signage may be altered or replaced, resulting in display anomalies or security breaches that affect their functionality or security.
3. Architecture of Digital Signage System
A common architecture for signage systems consists of four layers: Application Layer, Management Layer, Network Layer and Device Layer.
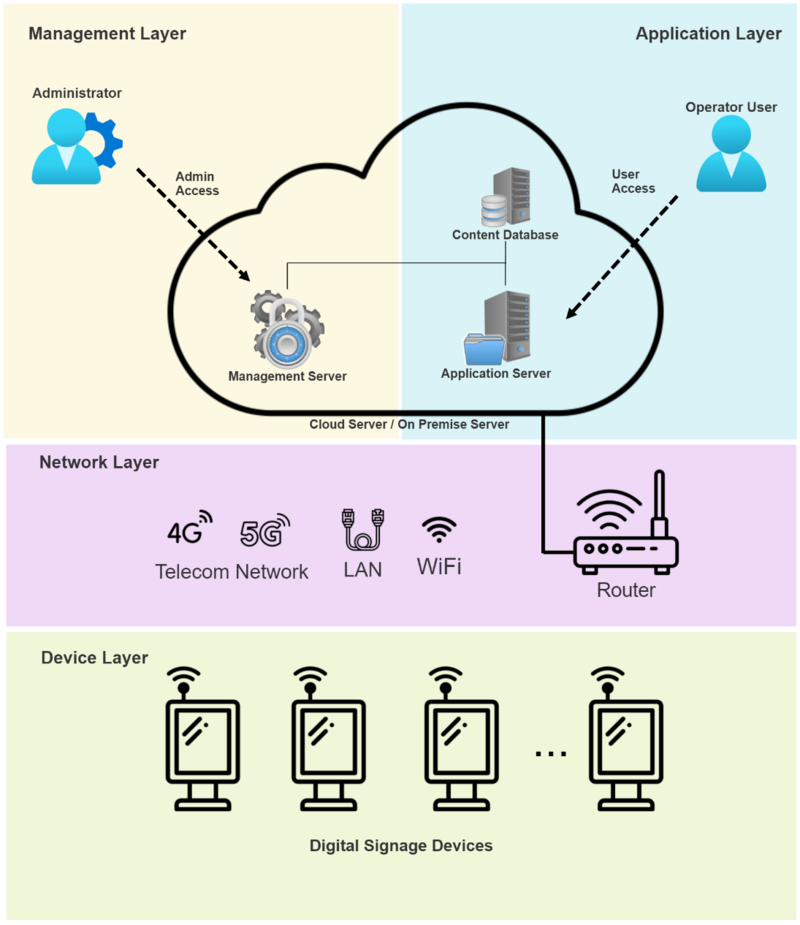
Common Architecture of Digital Signage
3.1 Application Layer
The Application Layer includes backend database containing signage data, business compliance information, and content management systems for content protection and data retention. In the guidelines, we will focus on the security of signage data and content compliance.
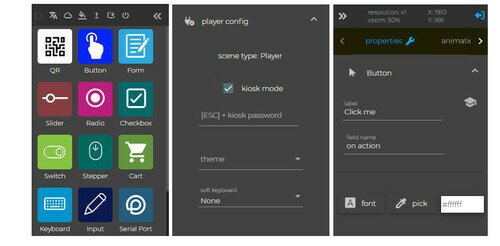
Multiple applications on application layer user interface (Image Source: digitalsignage.com)
By accessing the application server, operators can deploy or adjust the content information displayed on signage devices for optimal presentation.
3.2 Management Layer
The Management Layer, usually through the on-premises server or cloud server, involves device management (firmware, configuration, system updates), event and data monitoring, and maintenance. The guidelines focus on the security of the management system and user operations.
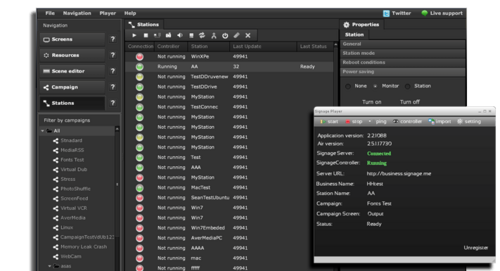
Management layer for multiple digital signage devices user interface (Image Source: digitalsignage.com)
By accessing the management server, administrators can manage one or more signage devices to perform device management and event monitoring.
3.3 Network Layer
This includes the transport payload of the signage using various communication technologies and protocols, such as Wi-Fi, LAN, and 4G/5G, along with security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection. These technologies must ensure stable and reliable data transmission in various environments.
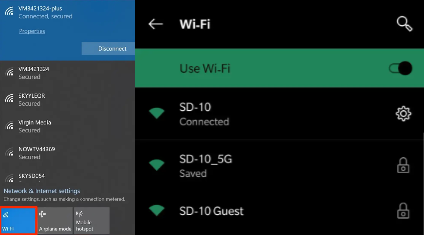
Digital signage are connected and managed by wireless protocols such as Wi-Fi through network settings in its underlying operating system (Image Source: androidguys)
3.4 Device Layer
The Device Layer is the starting point of digital signage, including the physical devices of the signage and the included physical interfaces, etc.

Users can interact through user interface of the digital signage (Image source: iStockPhoto)
4. Security Best Practice
Categorizing the digital signage system into application, management, network, and device layers helps in comprehensively understanding and managing potential security risks. This layered approach allows for targeted security measures to be implemented at each level, addressing specific threats and challenges, thereby enhancing overall security and system reliability.
4.1 Application Layer
| A. Data Privacy Security | |
|---|---|
| Data Protection |
|
| B. Standards and Compliance | |
| Data Custody |
|
| C. Content Management | |
| Content Protection |
|
| Data Retention |
|
4.2 Management Layer
| A. Device Management | |
|---|---|
| Device Security |
|
| System Security |
|
| Account Security |
|
| B. Data and Log Event Monitoring | |
| Incident Response and Handling |
|
| Monitoring and Log Management |
|
| Risk Assessment and Mitigation |
|
4.3 Network Layer
| A. Network Security | |
|---|---|
| Network Security |
|
| B. Wireless Security | |
| Wireless Security |
|
4.4 Device Layer
| A. Physical Security | |
|---|---|
| Physical Security |
|
| B. External Interface Port Access Control | |
| External Interface Port Access Control |
|
| C. Initial Configuration | |
| Initial Configuration |
|
5. Conclusion and Recommendation
Given the sophisticated systems of the digital signage itself, also the connection between signage and organisation’s internal system, it also creates entry points for potential cyber threats.
HKCERT recommends that users and business owners adopt a holistic approach to mitigate the associated security risks in each layer of digital signage ecosystem.
In addition to the above, attention should be given to the training of operators of digital signage. Safety awareness training should be provided to all users with reference to clear safety and security usage contingency guidelines and best practices to enhance users' understanding of safety best practices.
Furthermore, it's crucial to emphasize vendor management by selecting vendors that prioritize security in their products and services. Regularly review the security policies of third-party vendors interacting with digital signage systems to ensure comprehensive protection.
6. Reference
Related Tags
Share with
