Deepfake: Where Images Don't Always Speak Truth
"Deepfake" is the combination of "Deep learning" and "Fake". It utilizes deep learning techniques to train on vast amounts of data, including facial images, voices, and videos. This data is used to mimic and learn the characteristics, movements, and sounds of different individuals. Then, artificial intelligence (AI) technology is employed to create fake content, including fake images, voices, and videos, thus enabling functions like AI Face Swapping and Voice Cloning.

AI Face Swapping
AI Face Swapping is a technique that swaps a person's face with another person's face. This technology executes face swapping through facial recognition and facial capture. Nowadays the face swapping process can be easily done using a single image of the person's frontal face. AI can track the position and orientation of user's face and seamlessly fit it with the swapped face, even if the user's head is in motion. There are currently three main forms of AI face swapping:
1. Replace your face with the face in a photo: Replacing the face of a person in front of the camera with the face in a photo.
Source: HKCERT YouTube Channel
2. Apply your expression to a photo: Capturing the expression changes of a person in front of the camera, including the expression movements of lips, eyes, eyebrows, cheeks, and head, and reflecting these expressions onto another person's face in a photo. In this way, the viewer will feel as if he or she is communicating with the real person in the photo.
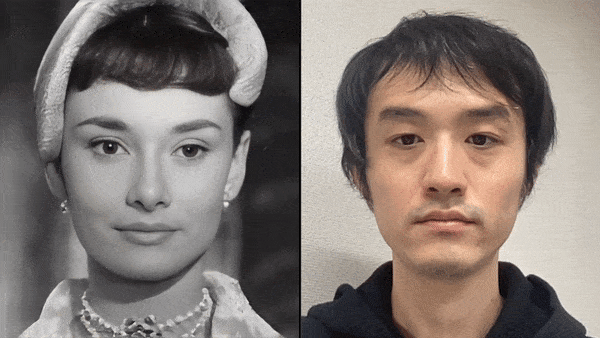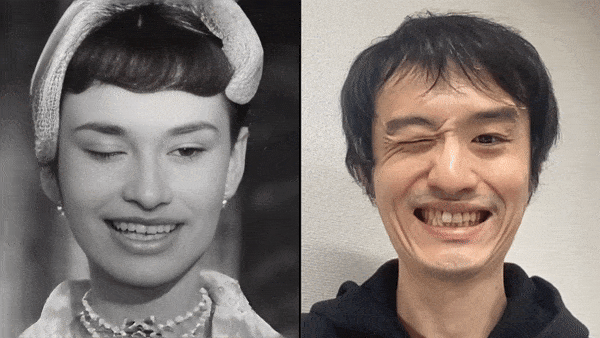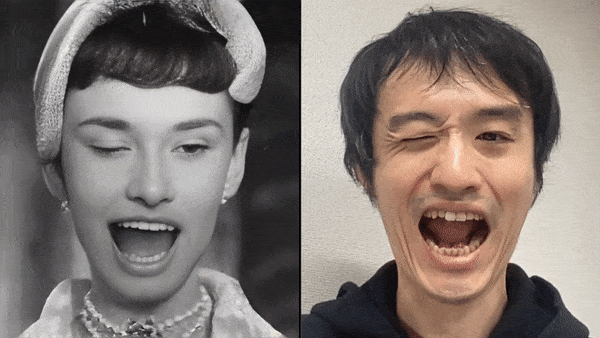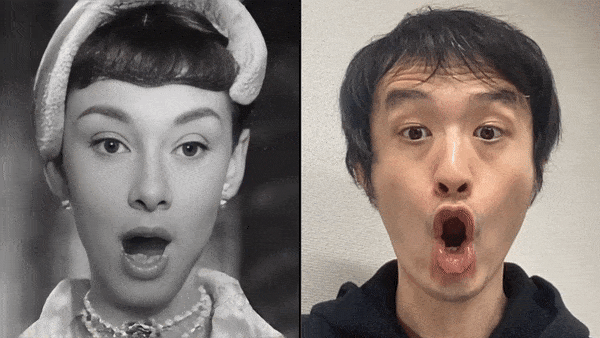
Source: Xpression Camera Demo
3. Generate facial expression from audio: Generating facial expressions and head movements of people in a photo based on recorded or real-time voice input, and converting the photo into a video that looks as if the person in the photo is speaking the voice input by the user. However, this technology is still in the research stage and has many limitations.
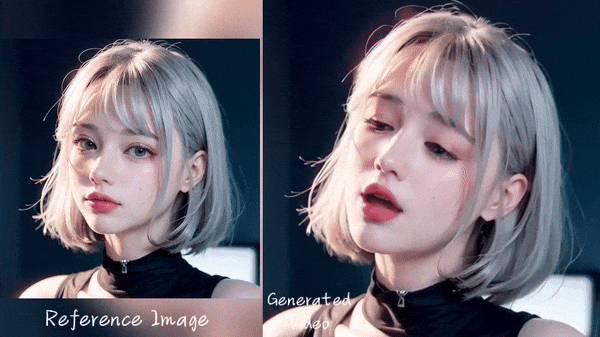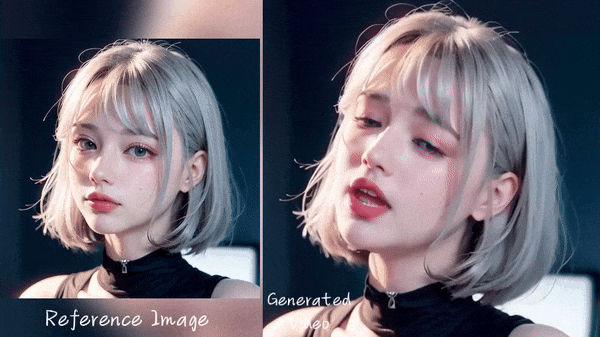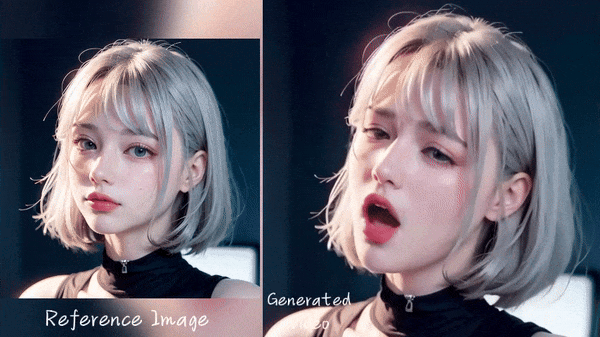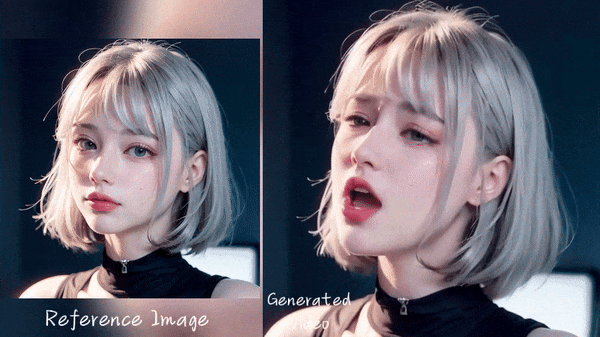
Source: Emote Portrait Alive (EMO) demo
The effectiveness of AI Face Swapping technology varies depending on the context of its application. In addition to editing prerecorded videos, some tools can even swap faces in real-time meetings. Generally, this technology produces realistic swapping effects that are difficult to distinguish from reality.
Voice Cloning
Voice cloning is a technology that uses AI to replicate voices. The cloned voice would sound like the original’s person voice in real life, including the speed, pitch, accent, and style. There are two types of implementations for voice cloning:
1. Text to Speech: User inputs text, and the AI system reads it out using the replicated voice.
2. Speech to Speech: User inputs their own voice, and the original voice is replaced with the replicated voice.
Voice cloning requires large amounts of training data (usually more than 10 hours of recording of the target’s voice to be cloned) and long training time (usually more than 10 hours, depending on the hardware) to obtain a high-quality voice replication.
Through AI Face Swapping and Voice Cloning, combined with massive data training, we can create lifelike replicas of anyone in the AI system. These replicas have both visual and auditory effects that are extremely realistic, achieving a seamless integration.
New Threats to Cyber Security
Despite the positive applications of deepfake technology in entertainment and healthcare, such as digitally recreating the images of deceased actors or reproducing the voices of people who have lost their voices due to illness or accidents, the most widely known usage of deepfake is to create fake videos or audios of celebrities to disseminate false or misleading information. Other abusive usages involve sexual imagery and fraud. Therefore, the danger of deepfake technology cannot be ignored, and this danger has been fully demonstrated in some real cases.
Examples of Recent Incidents
1. In August 2023, A criminal group was arrested for using deepfake to fake their identities to apply for loans.
Source (Chinese only): Ming Pao
2. In January 2024, a fake video surfaced featuring Hong Kong Chief Executive John Lee selling investment products, where the criminal used deepfake software to generate a fake voice of John Lee to make the video appear more authentic.
Source (Chinese only): Ming Pao
3. In February 2024, Hong Kong police reported a case where a multinational company's financial officer was deceived in a video conference. The criminals used deepfake technology to impersonate the company's chief financial officer, thereby defrauding the company of 200 million Hong Kong dollars.

Source (Chinese only): HK01
4. In February 2024, a Ukraine YouTuber discovered that her voice and face was stolen and being used in internet celebrity of selling good in Chinese social media using deepfake.
Source (Chinese only): HKET
Impact of Abusive Deepfake
Numerous deepfake software applications are available on today’s Internet, providing user-friendly interfaces for operation. Criminals can easily use this software to generate deepfake content even through cloud services. This accessibility makes it easy to create and spread deepfake content on the internet.
What is even more concerning is that deepfake technology may even bypass biometric security systems (such as facial or voice recognition), further increasing the risk of cyber
security. In addition, the misuse of deepfake technology may induce more phishing and internet frauds, false and misleading information, as well as bring trust and reputation crisis.
Phishing and Internet Fraud
Cases originating from Hong Kong and globally are concerning. Deepfake technology enables criminals to create more sophisticated phishing attacks. In the past, phishing attacks primarily relied on written messages. However, with the aid of deepfake technology, criminals increasingly use this technology to impersonate others and engage in fraudulent activities towards victims' relatives or colleagues. Particularly in an era where video calls and video-based communication are commonplace, fraudsters are further incentivized to produce more deepfake videos to deceive victims.
False and misleading information
Criminals produce deepfake videos impersonating celebrities, politicians, officials, etc., to disseminate false or misleading information, such as fake investment advice, false shares or statements, misleading victims' decision-making, and even creating social conflicts.
Trust and Reputation Crisis
Deepfake content has the potential to create a climate of distrust on the internet. As Deepfake can be challenging to distinguish, if there is a plethora of such videos online, genuine information will also be affected. Since people cannot easily discern whether the information they receive is mixed with deepfake content, ultimately leading to distrust in any information to prevent being deceived.
Additionally, deepfake content will replace the traditional fake videos, such as creating indecent, vulgar, or violent videos, leading viewers to believe that the victims are involved in certain activities, even if they are skeptical, it will damage the victim's reputation.
How to Spot Deepfake?
Identifying deepfake technology is quite challenging. Although there are online tools which claim to be able to detect the use of Deepfake in video, the key to distinguishing authenticity still lies in public awareness of security. Especially in a real time video scenario, such as in a video call or online conference, so we need to always remain vigilant. Below are some identification tips provided by HKCERT:
If you receive a suspicious video call, you can take the following measures:
Interfering with Deepfake Recognition Function
1. Ask the person to slowly cover their face with their hand. The original face may be revealed because the facial recognition algorithm in the deepfake software may fail to recognise a covered human face.

2. Request the person to move the camera around to capture another person. Deepfake software may misidentify the person to be replaced, leading to instant changes in the faces of both parties, being repeatedly replaced.
Paying Attention to the Detail of the Person’s Face
3. Observe the facial details of the person to identify any abnormalities when moving their head.
4. Check the skin colour, as facial color may differ from other parts of the body (e.g., neck, shoulders).
5. Pay attention to the person's skin texture, checking for excessive smoothness or too many wrinkles.
6. Focus on facial features for any unnatural features. For example:
- l Whether the beard and hairstyle look authentic;
- l Whether the person’s eyes appear natural;
- l Whether facial expressions are too stiff;
- l Whether there is any unreasonable expression when speaking, e.g. a serious expression on a relaxed face.
7. Observe whether the body below the head or background objects remain fixed.
Test the Person’s Reaction or Response
8. Ask questions about the fact that is known only between you and other person in order to verify his/her identity.
Reference
- Implications of Deepfake Technologies on National Security
- The Rise of Deepfake: Understanding Its Implications, Ethics & Mitigation Plan
- EMO: Emote Portrait Alive – Generating Expressive Portrait Videos with Audio2Video Diffusion Model under Weak Conditions
Related Tags
Share with


